With the depletion of fossil energy, the development of renewable resources is imminent. Plant fiber resources, with its wide range of sources and huge reserves, is an important treasure house of energy. Many important chemical raw materials and products can be derived from plant fiber raw materials. Among them, 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF) is active in chemical properties and can be used to prepare various derivatives through reactions such as oxidation, hydrogenation and condensation, and is one of the important fine chemical raw materials. 5-HMF is dehydrated from glucose or fructose, and fructose can be obtained from glucose isomerization. Therefore, the premise of the widespread application of 5-HMF is rich glucose raw materials. In particular, the direct extraction and preparation of glucose in fiber raw materials is of great significance. At the same time, the removal of lignin in plant fiber raw materials to obtain cellulosic materials is of great significance for the use of natural polymers.
Recently, Wang Tianfu, a researcher of the 1000-person plan of the Resource Chemistry Research Institute of the Xinjiang Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used a typical solid heteropoly acid (silicotungstic acid, phosphotungstic acid, phosphomolybdic acid) as a catalyst in γ-valerolactone/ In the water solvent system, the lignin in the log wood powder was effectively removed, and a cellulose-rich material was obtained. The material characterization results show that the heteropoly acid effectively removes the lignin from the log wood powder and has almost no effect on other components in the wood. And with the removal of lignin, more functional groups are exposed on the surface of the material, which has a positive significance for the modification of wood-based materials.
Further optimized enzyme degradation experiments showed that the cellulose substrate material after lignin removal can be enzymatically degraded to glucose under fairly mild conditions and can be used as the upstream material of glucose. It is worth emphasizing that the wood powder used in this experiment was not subjected to any pretreatment, so the study has important implications for the direct use of plant resources.
The research results were published in the international engineering journal Bioresource Technology. The first author of the article was Zhang Libo, a doctoral student. The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the 1000-member plan of the Central Organization Department.
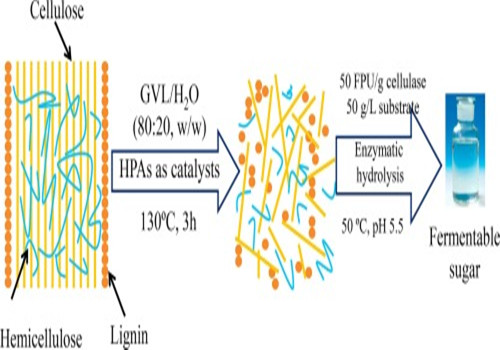
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the degradation of lignin in wood powder by enzymatic degradation of heteropoly acid and preparation of glucose
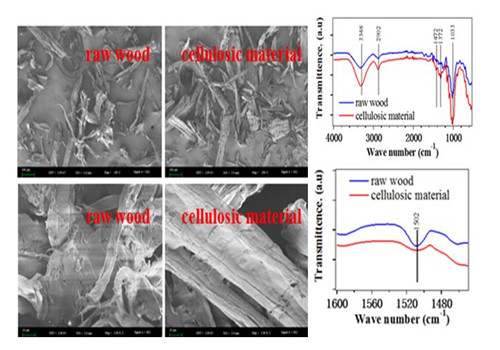
Fig.2 Characterization of cellulosic material and wood flour after lignin removal
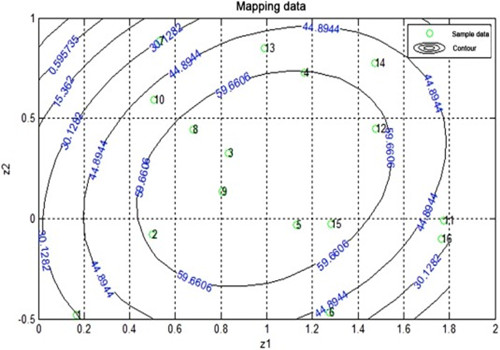
Fig. 3 Optimization of enzymatic degradation of cellulose
Wall Lamp,Plug In Wall Lamp,Led Wall Lamp,Solar Interaction Wall Lamp
Land of Lights Electric Appliance Co., LTD , https://www.loloutdoorlight.com