With the continuous development and advancement of mold industry technology, new materials and new processes are constantly emerging. Choosing the right cutting fluid in the CNC machining process of mold parts is crucial for ensuring product processing quality, improving processing efficiency and reducing environmental pollution. .
The cutting fluid is also commonly referred to as “coolantâ€. In addition to lubrication, cooling, chip removal, and rust prevention, it also has anti-foam, environmentally friendly, and antibacterial functions. The choice of cutting fluid is related to the surface quality and machining accuracy of the workpiece, and is also closely related to the material to be processed, the machining process and the tool material. The article discusses the relationship between the common materials of CNC tools and the selection of cutting fluids. It is designed to help engineers and technicians use cutting fluids correctly and use CNC tools effectively.
Typical materials for CNC tools:
1 .1 high speed steel:
High-speed steel is a high-alloy tool steel with a large amount of alloying elements such as tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo), chromium (Cr), and vanadium (V). High-speed steel has high hardness (62HRC ~ 67HRC) and heat resistance, and can cut at cutting temperatures up to 500 ~ 650 °C; high-speed steel has high strength (bending strength is 2 to 3 times that of ordinary cemented carbide) , 5 to 6 times of ceramics, good toughness, can be used in applications with impact and vibration; it can be used to process a wide range of materials such as non-ferrous metals, structural steels, cast irons, and superalloys. High-speed steel is easy to manufacture and has a sharp cutting edge. It is suitable for the manufacture of various types of tools. It is especially suitable for the manufacture of complex tools such as drills, broaches, forming tools and gear tools.
High-speed steel can be divided into ordinary high-speed steel and high-performance high-speed steel according to cutting performance; it can be divided into smelting high-speed steel and powder metallurgy high-speed steel according to the manufacturing process.
1. 2 Cemented carbide:
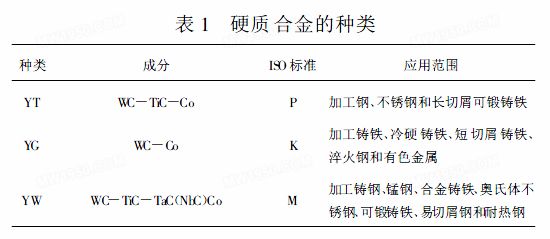
Cemented carbide is a powder metallurgy product sintered with high hardness, refractory metal carbide (WC, TiC, etc.) and metal binder (Cr, Ni, etc.) under high temperature conditions. The hardness of cemented carbide ranges from 89HRA to 93HRA, and its hardness is 77HRA to 85HRA at 760 °C. Carbide can also be cut at 800~1 000 °C. The tool life is several times to several tens of times higher than that of high speed steel tools. A variety of materials including hardened steel can be processed. However, the strength and toughness of cemented carbide are worse than that of high-speed steel. The impact toughness at normal temperature is only 18 to 130 of high-speed steel. Therefore, the ability of hard alloy to withstand cutting vibration and impact is poor. Table 1 shows several types of cemented carbide.
1 .3 Ceramic knives:
Ceramic knives have high hardness, wear resistance and good high temperature mechanical properties. They have low affinity with metals, are not easy to bond with metals, and have good chemical stability. Ceramic tools are mainly used in the cutting of steel, cast iron and its alloys and difficult-to-machine materials. They can be used for ultra-high-speed cutting, high-speed cutting and hard material cutting.
1 .4 superhard tool:
Superhard materials refer to synthetic diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN for short), and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and polycrystalline cubic nitride shed (PCBN) which are sintered by using these powders and binders.
Superhard materials have excellent wear resistance and are mainly used for high speed cutting and machining of difficult-to-cut materials.
2 Types of common cutting fluids
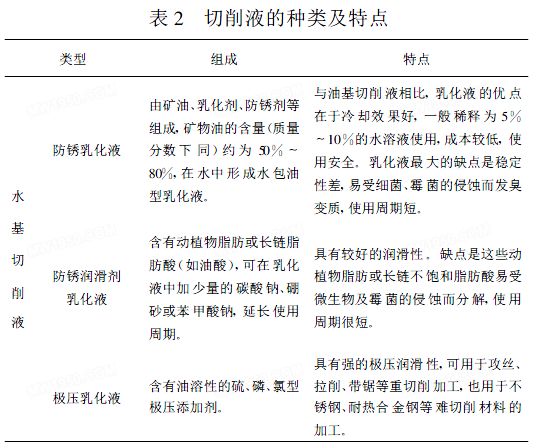
In order to meet different processing requirements, there are many types of cutting fluids. According to chemical composition and state, it can be divided into two types: water-based cutting fluid and oil-based cutting fluid. Generally, a cutting fluid diluted with water is called a water-based cutting fluid, and a cutting fluid that is not required to be diluted with water is called an oil-based cutting fluid. The water-based cutting fluid is mainly cooled and has poor lubrication performance. Commonly used water-based cutting fluids include: rust-proof emulsion, rust-proof lubricant emulsion, extreme pressure emulsion, micro-emulsion, etc.; oil-based cutting fluid for lubrication Mainly, the cooling effect and cleaning effect are poor. Commonly used oil-based cutting fluids are: pure mineral oil, fatty oil (or oily additive) + mineral oil, inactive extreme pressure cutting oil, active extreme pressure cutting oil, etc. The composition and application characteristics of several main cutting fluids are shown in Table 2.

3 Reasonable selection of cutting fluid
3 .1 high speed steel cutter:
This material is a high-grade alloy steel based on chromium, nickel, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium (some also containing aluminum). Their heat resistance is significantly higher than that of tool steel, allowing a maximum temperature of 600 °C. Compared with other high temperature resistant metal and ceramic materials, high speed steel has a number of advantages, especially its high toughness, suitable for geometrically complex workpieces and continuous cutting, and high speed steel has good machinability and The price is easily accepted.
Due to the poor red hardness of high speed steel tools, cutting fluids are required for use. Oil-based cutting fluids or emulsions are recommended for low and medium speed cutting. In high-speed cutting, it is preferable to use a water-based cutting fluid because of the large amount of heat generation. If oil-based cutting fluid is used, it will produce more oil mist, pollute the environment, and it will easily cause burns on the workpiece, the processing quality will decrease, and the tool wear will increase. In addition, extreme pressure aqueous solution or extreme pressure emulsion is recommended for roughing, while extreme pressure emulsion or extreme pressure cutting oil is used for finishing to reduce friction, improve surface quality and precision, and extend tool life.
3 .2 Carbide tools:
Cemented carbide is composed of tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TiC), tantalum carbide (TaC) and 5% to 10% cobalt. Its hardness is much higher than that of high speed steel. The maximum allowable working temperature is up to 1 000 °C. It has excellent wear resistance and can reduce the bond between chips when processing steel materials.
Due to the good red hardness of cemented carbide tools, dry machining is generally used without machining fluids when machining general materials. However, in dry cutting, the temperature rise of the workpiece is high, which makes the workpiece susceptible to thermal deformation and affects the machining accuracy of the workpiece. Moreover, cutting is performed without a lubricant, and since the cutting resistance is large, the power consumption is increased, and the wear of the tool is also accelerated. Carbide tools are more expensive, so from an economic point of view, dry cutting is not cost effective.
When selecting the cutting fluid, consider the sensitivity of the cemented carbide to the sudden heat, and make the tool evenly heated as much as possible, otherwise it will cause chipping. Generally, oil-based cutting fluids have poor thermal conductivity, which makes the tool quenching less dangerous than water-based cutting fluids. Therefore, oil-based cutting fluids containing anti-wear additives are generally preferred. When cutting with a cutting fluid, pay attention to evenly cooling the tool. It is best to pre-cool the tool before starting the cutting. For high-speed cutting, it is necessary to spray the cutting zone with a large flow of cutting fluid to avoid chipping caused by uneven heating of the tool, and to reduce oily smoke pollution caused by evaporation caused by excessive temperature.
3 .3 Ceramic knives:
This material is made of alumina, metal and carbide sintered at high temperature. Its high temperature wear resistance is better than that of hard alloy, so dry cutting is generally used. Water-based cutting fluids are often used in view of uniform cooling and avoiding excessive temperatures, but it is best to continuously and adequately cast without interruption.
3 .4 Diamond Tools:
With extremely high hardness, dry cutting is generally used. To avoid excessive temperatures, like ceramic materials, water-based cutting fluids are used in many cases.
4 Conclusion
Reasonable selection of cutting fluid according to different tool materials can not only improve the surface quality and machining accuracy of the workpiece, but also reduce the thermal deformation of the workpiece and the wear of the tool, improve the durability of the tool, reduce the production cost, and improve the production efficiency. It should be taken seriously in production.
Power Station Valve,Power Station Gate Valve,Power Station Valve Types,Power Station Valves
Haogong Valve Co Ltd , https://www.haogongvalve.com